MatheAss 10.0 − 3-dim. Geometry
Coordinate systems
With this program, three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates can be converted into spherical coordinates or cylinder coordinates and vice versa.
cartesian polar cylindrical x = 1 r = 1.7320508 ρ = 1.4142136 y = 1 φ = 45° φ = 45° z = 1 Θ = 35,26439° z = 1
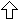 Platonic bodies
Platonic bodies
The program calculates the five Platonic bodies tetrahedron, hexahedron, octahedron, dodecahedron and icosahedron if edge length, surface height, room height, insphere radius, umbelly radius, volume or surface are given.
Example: Dodecahedron
Given:
¯¯¯¯¯¯
Face Diagonal d = 2
Results:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Edge a = 1,236068
Face Altitude h = 1,902113
Circumradius rc = 1,7320508
Inradius ri = 1,3763819
Volume V = 14,472136
Surface S = 31,543867
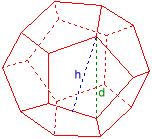
 Other bodies
Other bodies
The program calculates all the sizes of a regular prism, a vertical circular cylinder, a regular pyramid, a vertical circular cone or a sphere if two of them are given.
Example: Circular cone
Given:
¯¯¯¯¯¯
Volume V = 1
Base B = 1
Results:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Radius r = 0,56418958
Altitude h = 3
Apothem s = 3,0525907
Lateral Surface L = 5,4105761
Surface S = 6,4105761
Straight Line by 2 points
Line through A(1|1|1), B(2|5|6)
Parametric representation
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧ 1 ⎫ ⎧ 1 ⎫
x = ⎪ 1 ⎪ + t·⎪ 4 ⎪
⎩ 1 ⎭ ⎩ 5 ⎭
Distance from origin
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
d = 0,78679579
Position to the xy plane
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Projection : 4·x - y = 3
Inters.Point: S1(0,8|0,2|0)
Inters.Angle: 50,490288°
Position to the yz plane
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Projection : 5·y - 4·z = 1
Inters.Point: S2(0|-3|-4)
Inters.Angle: 8,8763951°
Position to the xz plane
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Projection : 5·x - z = 4
Inters.Point: S3(0,75|0|-0,25)
Inters.Angle: 38,112927°
Plane by 3 points
Plane through the points:
A(1|2|3), B(2|3|3), C(1|0|1)
Point-slope-form:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧ 1 ⎫ ⎧ 1 ⎫ ⎧ 0 ⎫
x = ⎪ 2 ⎪+r·⎪ 1 ⎪+s·⎪ 1 ⎪
⎩ 3 ⎭ ⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
Equation in coordinates:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
x - y + z = 2
Distance from origin:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
d = 1,1547005
Trace points:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
Sx(2|0|0)
Sy(0|-2|0)
Sz(0|0|2)
Sphere by 4 points
Sphere through the points:
A(1|0|0), B(0|2|0),
C(0|0|3), D(1|0|1)
Normal form:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
⎧ -> ⎧-2,5 ⎫ ⎫2
K : ⎪ x - ⎪-0,5 ⎪ ⎪ = 12,75
⎩ ⎩ 0,5 ⎭ ⎭
Center and radius:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
M(-2,5|-0,5|0,5)
r = 3,5707142
 Intersections in the space
Intersections in the space
The program calculates the sections of straight lines, planes and spheres.
Two Straight Lines
-> ⎧ 5 ⎫ ⎧ 0 ⎫
g : x = ⎪ 0 ⎪ + r·⎪ 1 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
-> ⎧ 0 ⎫ ⎧ 1 ⎫
h : x = ⎪ 5 ⎪ + s·⎪ 0 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
Intersection point: S(5|5|5)
Intersection angle: 60°
Distances from origin :
d(O,g)=5 d(O,h)=5
Plane and Straight Line
Plane E :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
E : x + y + z = 5
Line g :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧ 5 ⎫ ⎧ 0 ⎫
g : x = ⎪ 0 ⎪ + r·⎪ 1 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
Intersection point :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
S(5|0|0)
Intersection angle :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
alpha = 54,73561°
Sphere and Straight Line
Sphere :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
K : M(5|5|5) , r = 5
Line :
¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧ 1 ⎫ ⎧ 1 ⎫
g : x = ⎪ 0 ⎪ + r·⎪ 1 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
Intersection points :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
S1(2,81867|1,81867|1,81867)
S2(8,51467|7,51467|7,51467)
Length of the chord :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
s = 9,8657657
Two Planes
Given the two planes:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
E1 : 5·x - 2·y = 5
E2 : 2·x - y + 5·z = 8
Intersection line:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
-> ⎧-11 ⎫ ⎧ 10 ⎫
g : x = ⎪-30 ⎪ + r·⎪ 25 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭
Distance from origin:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
d = 1,5057283
Intersection angle:
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
alpha = 65,993637°
Two Spheres
Given the two spheres: ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ K1 : M1(3|3|3) , r1 = 3 K2 : M2(1|1|1) , r2 = 3 Intersection circle: ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ M(2|2|2), r = 2,4494897 Intersection plane : ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ E : x + y + z = 6
Sphere and Plane
Plane :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
E : 5·x - 4·y + 5·z = -3
Sphere :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
⎧ -> ⎧ 1 ⎫⎫2
K : ⎪ x - ⎪ 2 ⎪⎪ = 16
⎩ ⎩ 3 ⎭⎭
Intersection circle :
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
M(1|1|1), r = 2
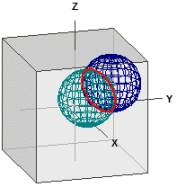
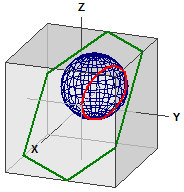
 Distances on the sphere
(New in version 9.0 from December 2021)
Distances on the sphere
(New in version 9.0 from December 2021)
The distance between two points on a sphere is calculated. The program is also suitable for converting decimal degrees into degrees, minutes and seconds (dms) and vice versa.
GPS decimal ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ Berlin : 52.523403, 13.4114 New York : 40.714268, -74.005974 GPS dms ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ Berlin : 52° 31' 24.2508" N, 13° 24' 41.0400" E New York : 40° 42' 51.3648" N, 74° 0' 21.5064" W . . . Distance ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ d = r · α [rad] = 6385,112